# Building on Windows
**Note that installing all the development prerequisites and libraries will require about 12 GB of free disk space. Please ensure this space is available on your `C:` drive before proceeding.**
This guide assumes you are on a 64-bit system. You might need to manually search out alternate download links should you desire to build Chatterino on a 32-bit system.
## Prerequisites
### Visual Studio
Download and install [Visual Studio 2022 Community](https://visualstudio.microsoft.com/downloads/). In the installer, select "Desktop development with C++".
Notes:
- This installation will take about 8 GB of disk space
- You do not need to sign in with a Microsoft account after setup completes. You may simply exit the login dialog.
### Qt
1. Visit the [Qt Open Source Page](https://www.qt.io/download-open-source).
2. Scroll down to the bottom
3. Then select "Download the Qt Online Installer"
4. Within the installer, Qt will prompt you to create an account to access Qt downloads.
Notes:
- Installing the latest **stable** Qt version is advised for new installations, but if you want to use your existing installation please ensure you are running **Qt 5.15.2 or later**.
#### Components
When prompted which components to install, do the following:
1. Unfold the tree element that says "Qt"
2. Unfold the top most tree element (latest stable Qt version, e.g. `Qt 6.5.3`)
3. Under this version, select the following entries:
- `MSVC 2019 64-bit` (or `MSVC 2022 64-bit` from Qt 6.8 onwards)
- `Qt 5 Compatibility Module`
- `Additional Libraries` > `Qt Image Formats`
4. Under the "Tools" tree element (at the bottom), ensure that `Qt Creator X.X.X` and `Debugging Tools for Windows` are selected. (they should be checked by default)
5. Continue through the installer and let the installer finish installing Qt.
Note: This installation will take about 2 GB of disk space.
Once Qt is done installing, make sure you add its bin directory to your `PATH` (e.g. `C:\Qt\6.5.3\msvc2019_64\bin`)
How to add Qt to PATH
1. Type "path" in the Windows start menu and click `Edit the system environment variables`.
2. Click the `Environment Variables...` button bottom right.
3. In the `User variables` (scoped to the current user) or `System variables` (system-wide) section, scroll down until you find `Path` and double click it.
4. Click the `New` button top right and paste in the file path for your Qt installation (e.g. `C:\Qt\6.5.3\msvc2019_64\bin` by default).
5. Click `Ok`
### Advanced dependencies
These dependencies are only required if you are not using a package manager
Boost
1. First, download a boost installer appropriate for your version of Visual Studio.
- Visit the downloads list on [SourceForge](https://sourceforge.net/projects/boost/files/boost-binaries/).
- Select the latest version from the list.
- Download the `.exe` file appropriate to your Visual Studio installation version and system bitness (choose `-64` for 64-bit systems).
Visual Studio versions map as follows: `14.3` in the filename corresponds to MSVC 2022. _Anything prior to Visual Studio 2022 is unsupported. Please upgrade should you have an older installation._
**Convenience link for Visual Studio 2022: [boost_1_84_0-msvc-14.3-64.exe](https://sourceforge.net/projects/boost/files/boost-binaries/1.84.0/boost_1_84_0-msvc-14.3-64.exe/download)**
2. When prompted where to install Boost, set the location to `C:\local\boost`.
3. After the installation finishes, rename the `C:\local\boost\lib64-msvc-14.3` (or similar) directory to simply `lib` (`C:\local\boost\lib`).
Note: This installation will take about 2.1 GB of disk space.
## Building
### Using CMake
#### Install conan 2
Install [conan 2](https://conan.io/downloads.html) and make sure it's in your `PATH` (default setting).
Adding conan to your PATH if you installed it with pip
_Note: This will add all Python-scripts to your `PATH`, conan being one of them._
1. Type "path" in the Windows start menu and click `Edit the system environment variables`.
2. Click the `Environment Variables...` button bottom right.
3. In the `System variables` section, scroll down until you find `Path` and double click it.
4. Click the `New` button top right.
5. Open up a terminal `where.exe conan` to find the file path (the folder that contains the conan.exe) to add.
6. Add conan 2's file path (e.g. `C:\Users\example\AppData\Roaming\Python\Python311\Scripts`) to the blank text box that shows up. This is your current Python installation's scripts folder.
7. Click `Ok`
Then in a terminal, configure conan to use `NMake Makefiles` as its generator:
1. Generate a new profile
`conan profile detect`
#### Build
Open up your terminal with the Visual Studio environment variables (e.g. `x64 Native Tools Command Prompt for VS 2022`), cd to the cloned chatterino2 directory and run the following commands:
```cmd
mkdir build
cd build
conan install .. -s build_type=Release -c tools.cmake.cmaketoolchain:generator="NMake Makefiles" --build=missing --output-folder=.
cmake -G"NMake Makefiles" -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release -DCMAKE_TOOLCHAIN_FILE="conan_toolchain.cmake" -DCMAKE_PREFIX_PATH="C:\Qt\6.5.3\msvc2019_64" ..
nmake
```
To build a debug build, you'll also need to add the `-s compiler.runtime_type=Debug` flag to the `conan install` invocation. See [this StackOverflow post](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/59828611/windeployqt-doesnt-deploy-qwindowsd-dll-for-a-debug-application/75607313#75607313)
To build with plugins add `-DCHATTERINO_PLUGINS=ON` to `cmake` command.
#### Deploying Qt libraries
Once Chatterino has finished building, to ensure all .dll's are available you can run this from the build directory:
`windeployqt bin/chatterino.exe --release --no-compiler-runtime --no-translations --no-opengl-sw --dir bin/`
Can't find windeployqt? You forgot to add your Qt bin directory (e.g. `C:\Qt\6.5.3\msvc2019_64\bin`) to your `PATH`
### Developing in Qt Creator
1. Open the `CMakeLists.txt` file by double-clicking it, or by opening it via Qt Creator.
2. You will be presented with a screen that is titled "Configure Project". In this screen, you should have at least one option present ready to be configured, like this:
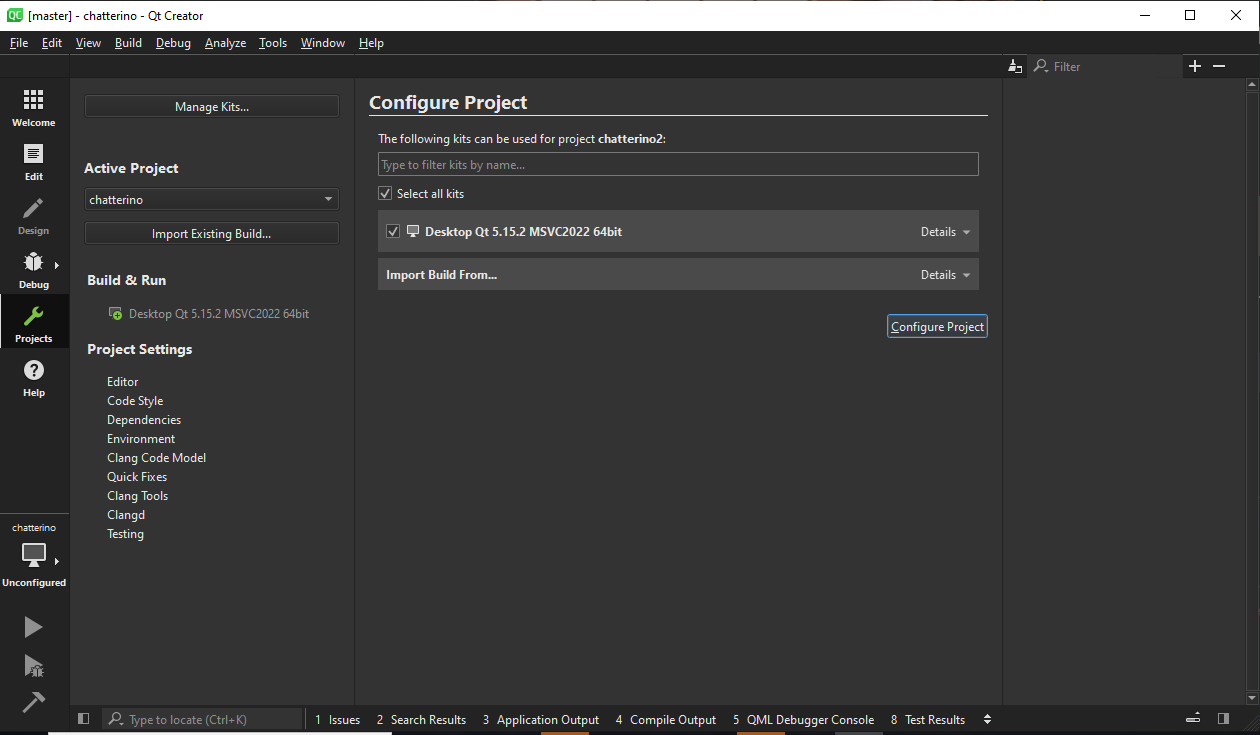
3. Select the profile(s) you want to build with and click "Configure Project".
#### Building and running
- In the main screen, click the green "play symbol" on the bottom left to run the project directly.
- Click the hammer on the bottom left to generate a build (does not run the build though).
Build results will be placed in a folder at the same level as the "chatterino2" project folder (e.g. if your sources are at `C:\Users\example\src\chatterino2`, then the build will be placed in an automatically generated folder under `C:\Users\example\src`, e.g. `C:\Users\example\src\build-chatterino-Desktop_Qt_6.5.3_MSVC2019_64bit-Release`.)
- Note that if you are building Chatterino purely for usage, not for development, it is recommended that you click the "PC" icon above the play icon and select "Release" instead of "Debug".
- Output and error messages produced by the compiler can be seen under the "4 Compile Output" tab in Qt Creator.
#### Producing standalone builds
If you build Chatterino, the result directories will contain a `chatterino.exe` file in the `$OUTPUTDIR\release\` directory. This `.exe` file will not directly run on any given target system, because it will be lacking various Qt runtimes.
To produce a standalone package, you need to generate all required files using the tool `windeployqt`. This tool can be found in the `bin` directory of your Qt installation, e.g. at `C:\Qt\6.5.3\msvc2019_64\bin\windeployqt.exe`.
To produce all supplement files for a standalone build, follow these steps (adjust paths as required):
1. Navigate to your build output directory with Windows Explorer, e.g. `C:\Users\example\src\build-chatterino-Desktop_Qt_6.5.3_MSVC2019_64bit-Release`
2. Enter the `release` directory
3. Delete all files except the `chatterino.exe` file. You should be left with a directory only containing `chatterino.exe`.
4. Open a command prompt and execute:
```cmd
cd C:\Users\example\src\build-chatterino-Desktop_Qt_6.5.3_MSVC2019_64bit-Release\release
windeployqt bin/chatterino.exe --release --no-compiler-runtime --no-translations --no-opengl-sw --dir bin/
```
5. The `releases` directory will now be populated with all the required files to make the Chatterino build standalone.
You can now create a zip archive of all the contents in `releases` and distribute the program as is, without requiring any development tools to be present on the target system. (However, the CRT must be present, as usual - see the [README](README.md)).
#### Formatting
To automatically format your code, do the following:
1. Download [LLVM 16.0.6](https://github.com/llvm/llvm-project/releases/download/llvmorg-16.0.6/LLVM-16.0.6-win64.exe)
2. During the installation, make sure to add it to your path
3. Enable Beautifier under `Extensions` on the left (check "Load on start" and restart)
4. In Qt Creator, Select `Tools` > `Options` > `Beautifier`
5. Under `General` select `Tool: ClangFormat` and enable `Automatic Formatting on File Save`
6. Under `Clang Format` select `Use predefined style: File` and `Fallback style: None`
### Building on MSVC with AddressSanitizer
Make sure you installed `C++ AddressSanitizer` in your VisualStudio installation like described in the [Microsoft Docs](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/cpp/sanitizers/asan#install-the-addresssanitizer).
To build Chatterino with AddressSanitizer on MSVC, you need to add `-DCMAKE_CXX_FLAGS=/fsanitize=address` to your CMake options.
When you start Chatterino, and it's complaining about `clang_rt.asan_dbg_dynamic-x86_64.dll` missing,
copy the file found in `\VC\Tools\MSVC\\bin\Hostx64\x64\clang_rt.asan_dbg_dynamic-x86_64.dll` to the `Chatterino` folder inside your `build` folder.
To learn more about AddressSanitizer and MSVC, visit the [Microsoft Docs](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/cpp/sanitizers/asan).
### Developing in CLion
_Note:_ We're using `build` instead of the CLion default `cmake-build-debug` folder.
Install [conan](https://conan.io/downloads.html) and make sure it's in your `PATH` (default setting).
Clone the repository as described in the readme. Open a terminal in the cloned folder and enter the following commands:
1. `mkdir build && cd build`
2. `conan install .. -s build_type=Debug`
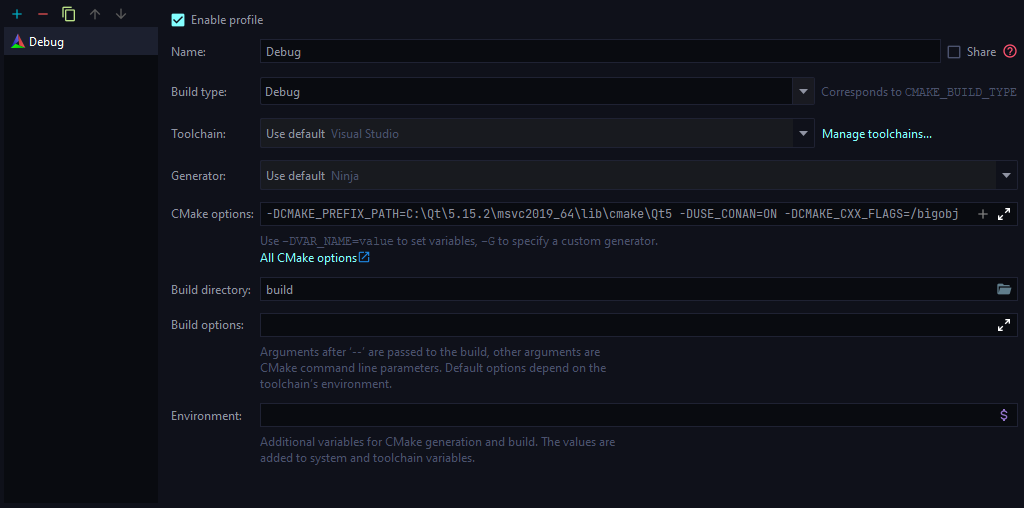
Now open the project in CLion. You will be greeted with the _Open Project Wizard_. Set the _CMake Options_ to
```text
-DCMAKE_PREFIX_PATH=C:\Qt\6.5.3\msvc2019_64\lib\cmake\Qt6
-DCMAKE_TOOLCHAIN_FILE="conan_toolchain.cmake"
```
and the _Build Directory_ to `build`.
Screenshot of CMake configuration
After the CMake project is loaded, open the _Run/Debug Configurations_.
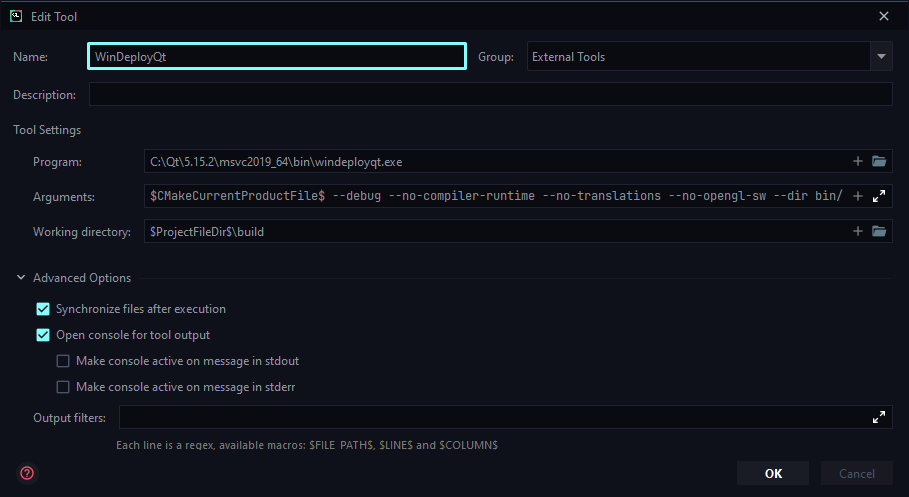
Select the `CMake Applications > chatterino` configuration and add a new _Run External tool_ task to _Before launch_.
- Set the _Program_ to `C:\Qt\6.5.3\msvc2019_64\bin\windeployqt.exe`
- Set the _Arguments_
to `$CMakeCurrentProductFile$ --debug --no-compiler-runtime --no-translations --no-opengl-sw --dir bin/`
- Set the _Working directory_ to `$ProjectFileDir$\build`
Screenshot of External tool
Screenshot of Chatterino configuration
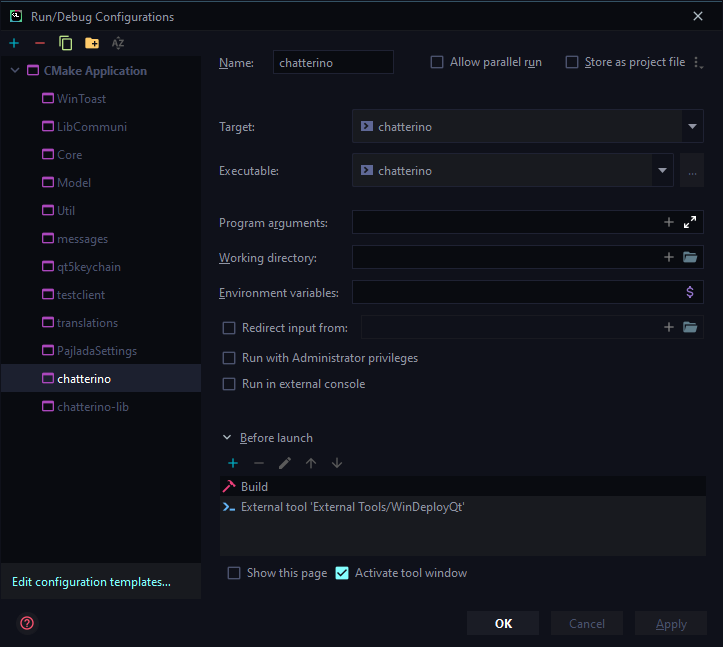
Now you can run the `chatterino | Debug` configuration.
If you want to run the portable version of Chatterino, create a file called `modes` inside `build/bin` and
write `portable` into it.
#### Debugging
To visualize Qt types like `QString`, you need to inform CLion and LLDB
about these types.
1. Set `Enable NatVis renderers for LLDB option`
in `Settings | Build, Execution, Deployment | Debugger | Data Views | C/C++` (should be enabled by default).
2. Use the official NatVis file for Qt from [`qt-labs/vstools`](https://github.com/qt-labs/vstools) by saving them to
the project root using PowerShell:
```powershell
(iwr "https://github.com/qt-labs/vstools/raw/dev/QtVsTools.Package/qt6.natvis.xml").Content.Replace('##NAMESPACE##::', '') | Out-File qt6.natvis
# [OR] using the permalink
(iwr "https://github.com/qt-labs/vstools/raw/1c8ba533bd88d935be3724667e0087fd0796102c/QtVsTools.Package/qt6.natvis.xml").Content.Replace('##NAMESPACE##::', '') | Out-File qt6.natvis
```
Now you can debug the application and see Qt types rendered correctly.
If this didn't work for you, try following
the [tutorial from JetBrains](https://www.jetbrains.com/help/clion/qt-tutorial.html#debug-renderers).